Understanding Core Concepts¶
At its core, SampleDB manages metadata about Objects. These objects can be close to anything, from samples and measurements in a typical laboratory setting to simulations, projects, or proposals. SampleDB administrators have full control over the specific types of objects their instances can manage.
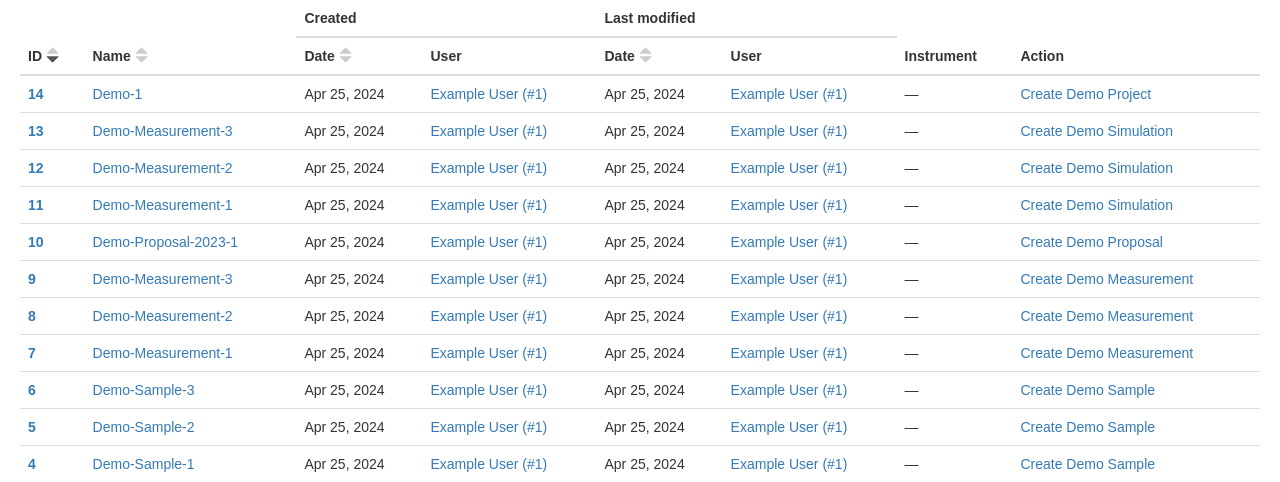
A list of objects¶
Every object in SampleDB is associated with a distinct set of metadata, including a name and other relevant information like the creation date of a sample or specific instrument settings. Therefore, when you intend to create a new object, you need to provide SampleDB with this metadata.
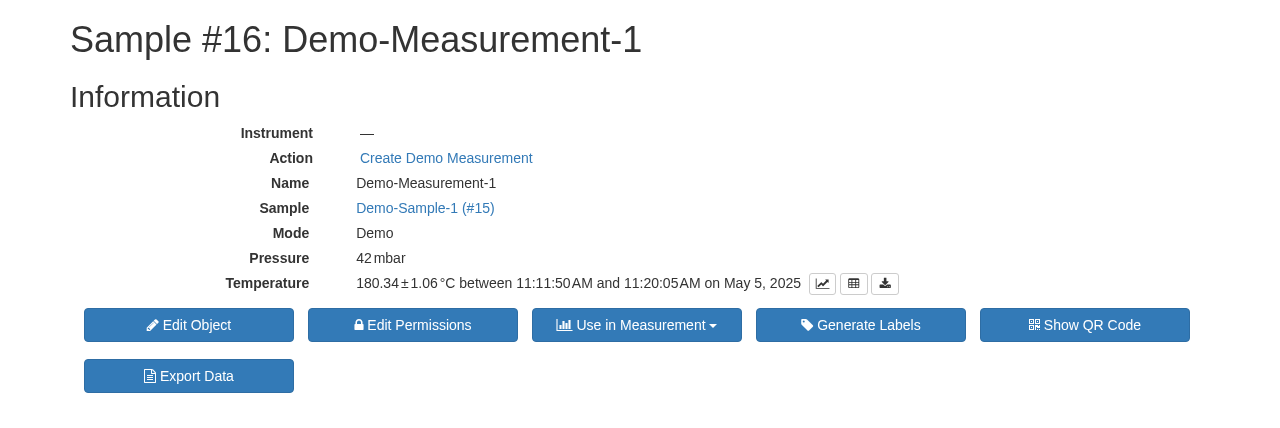
Object metadata¶
The way to do this is via an Action. While objects represent the things described by the metadata, actions represent the processes that create them. Therefore, an action could represent a specific type of measurement you want to perform. Administrators, instrument scientists, and even regular users can create new actions to represent new processes they want to keep track of. To do so, they need to configure a name, a few settings and then define a schema.
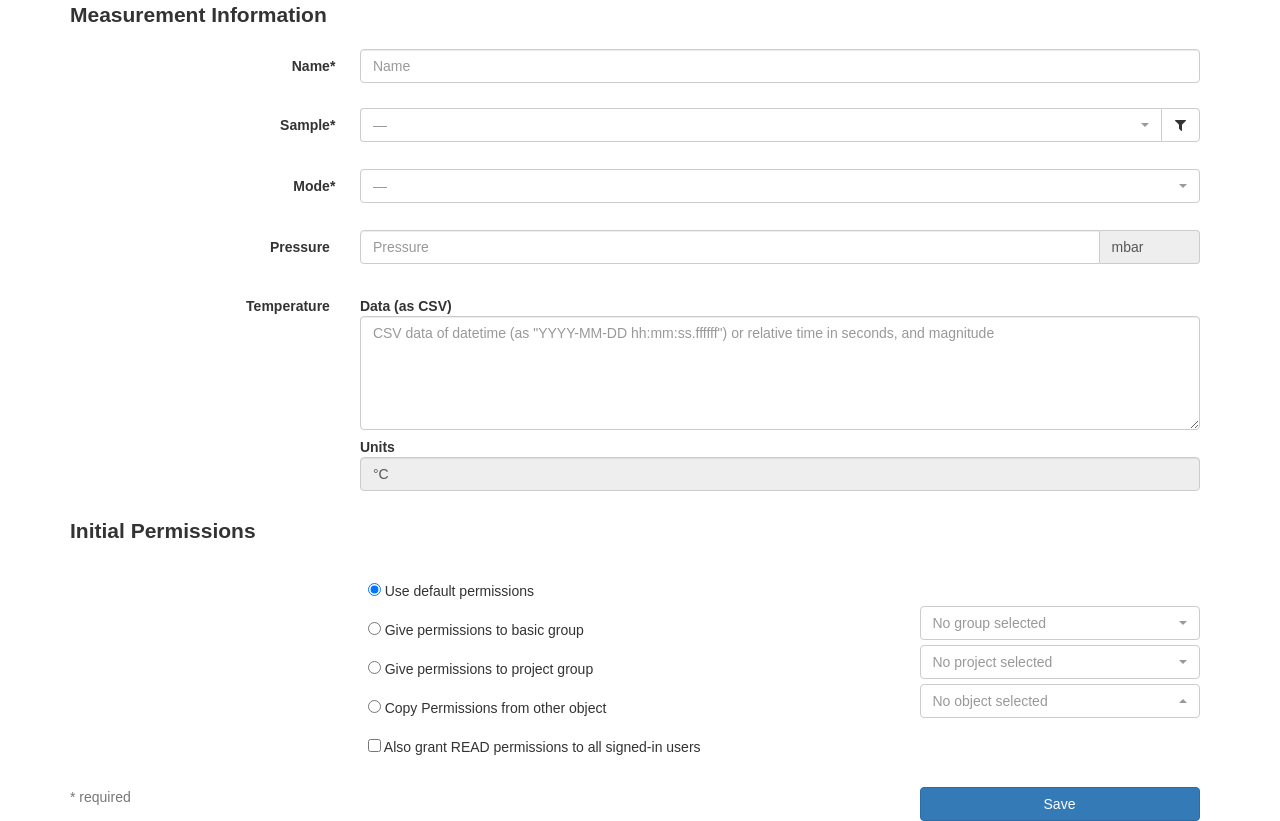
Entering object metadata¶
For every action, its Schema controls what metadata can and must be entered to create an object with that action. So the schema defines the metadata fields, their order, and some other settings for the action.
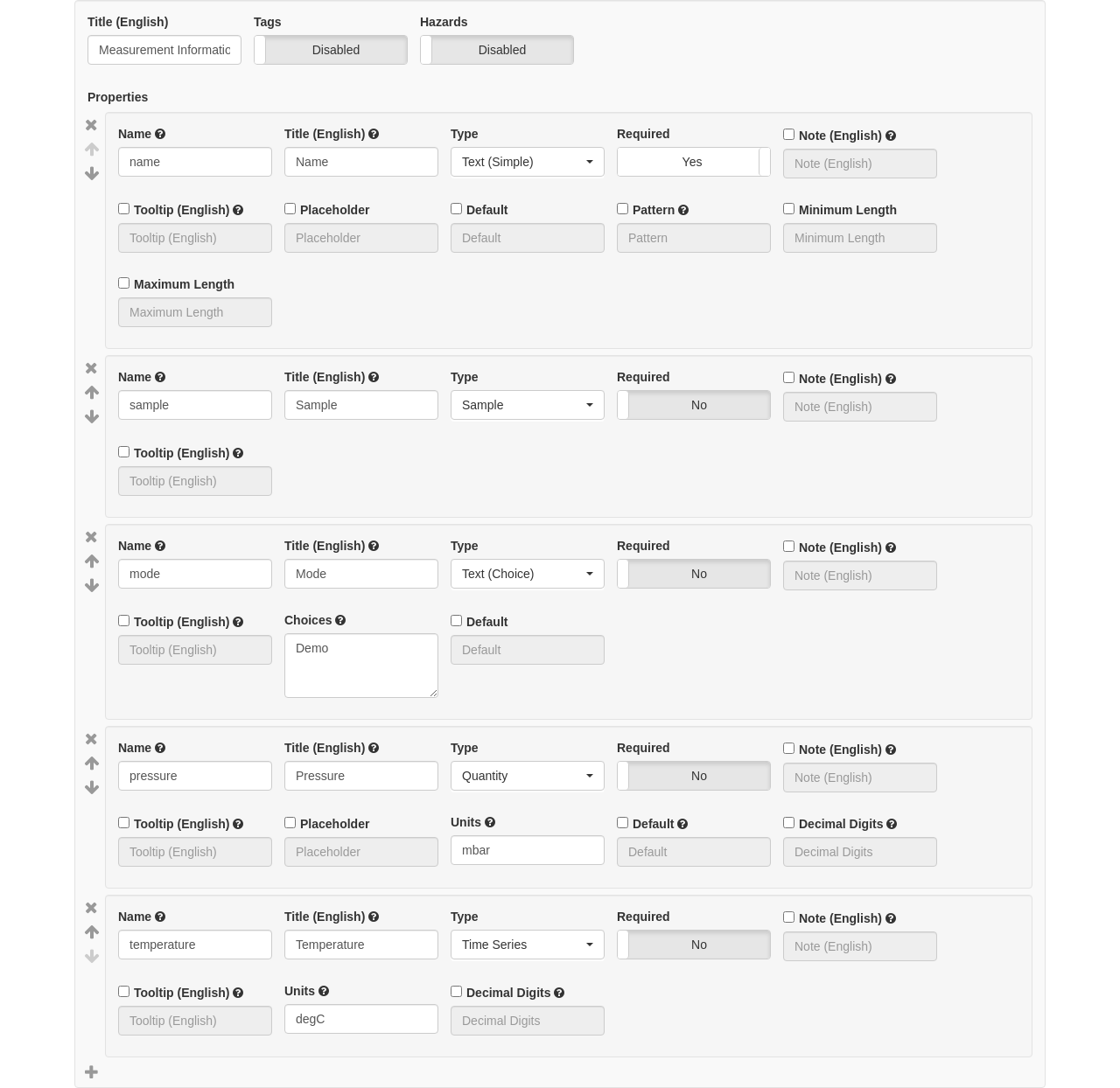
Editing an action using the schema editor¶
Lastly, every action belongs to an Action Type, which determines whether they create samples, measurements, or other types of objects. Administrators can configure these action types, which not only set the names of actions and objects but also control additional behavior. For example, they can decide whether to display a button for generating labels, which may be useful for samples but less so for simulations.
Summary
SampleDB is a tool for managing metadata about objects, such as samples and measurements.
Actions represent processes that create objects, such as a specific type of measurement.
Each action has a Schema that defines the metadata fields.
Actions are categorized into action types, which are configured by administrators.
See also
